The answer to this question isn’t straightforward and depends on various factors. Cocaine is a powerful stimulant and is known for its intense, albeit short-lived, effects. But what about its presence in the body? How long does cocaine really stay in your system?
This knowledge is crucial when it comes to drug testing and assessing the potential risks associated with cocaine use.
In this blog, we will get into the truth behind the lingering effects of cocaine. Whether you are concerned about passing a drug test or simply curious about the drug’s impact on your body, understanding its timeline in your system is essential.
One common misconception is that cocaine leaves the body quickly, within hours after use. However, the truth is more complex. Factors like metabolism, frequency of use, and the individual’s overall health can significantly impact the drug’s detection window.
We will break down the different drug tests used to detect cocaine, including urine, saliva, blood, and hair tests, and discuss how long cocaine can be detected in each.
Additionally, we will explore tips and strategies that may help speed up the elimination of cocaine from the body. Whether you are looking for accurate information or seeking guidance on drug use and detection, this blog will provide you with the insights you need to understand the truth about cocaine’s presence in your system.
Every step you take toward recovery matters!
The different drug tests used to detect cocaine:
Detecting cocaine use is essential for various purposes, including workplace screenings, probation monitoring, and addiction treatment. Different drug tests are employed to detect the presence of cocaine in the body, each with its own advantages and detection windows. We will explore the various drug tests used to identify cocaine use, including urine, saliva, blood, and hair tests.
1. Urine Tests:
Urine tests are one of the most common methods for detecting recent cocaine use. They are cost-effective, non-invasive, and offer a detection window of approximately 2-4 days after use. However, it’s worth noting that heavy or chronic use may extend this detection period, making urine tests less effective for those individuals.
2. Saliva Tests:
Saliva tests are gaining popularity due to their simplicity and non-invasiveness. They can detect cocaine within 1-2 days of use. While they are less prone to tampering and can be administered easily, they have a shorter detection window compared to urine and blood tests.
3. Blood Tests:
Blood tests are highly accurate and can detect cocaine within 1-2 days of use. They are often used in emergency situations, such as accidents or overdoses. However, they are less common for routine screenings due to their invasive nature and the short detection window.
4. Hair Tests:
Hair follicle tests provide the longest detection window, reaching up to 90 days after cocaine use. These tests are challenging to tamper with and can reveal a pattern of drug use over time. However, they are more expensive and may not detect very recent use.
The choice of test depends on factors like the detection window required and the specific needs of the situation. By being informed about these testing methods, we can better navigate the challenges of cocaine detection and its implications in various contexts.

It’s important to emphasize that attempting to cheat on a drug test is not only unethical but also illegal in many places. Tampering with a drug test can lead to severe consequences. Additionally, it’s crucial to address any concerns about substance use or addiction with a healthcare professional and seek appropriate support if needed. Overcoming addiction and making positive lifestyle changes should be the primary focus.
What factors affect detection time?
The detection time for cocaine in your system can be influenced by several factors, which include:
1. Frequency of Use:
How often you use cocaine plays a crucial role in the duration it remains detectable in your system. Chronic or heavy use can lead to a longer detection window because cocaine and its byproducts accumulate in your body over time.
2. Metabolism:
Individual metabolic variations are significant. A person with a faster metabolism is more likely to eliminate cocaine more swiftly than someone with a slower metabolic rate.
3. Overall Health:
The health of your liver and kidneys, responsible for processing and excreting substances such as cocaine, can impact the detection time. A robust and healthy organ system can process and remove drugs more efficiently.
4. Hydration:
Staying adequately hydrated can help expedite the elimination of cocaine metabolites. Dehydration, conversely, can slow down the elimination process.
5. Type of Test:
The choice of drug test employed (urine, blood, saliva, or hair) plays a pivotal role in determining the detection window. For instance, hair follicle tests generally offer a more extended detection period compared to urine tests.
It’s crucial to recognize that while these factors can influence the detection time, predicting the exact duration cocaine will remain detectable for a specific individual is challenging. Detection times are approximations and can differ substantially based on individual characteristics and unique circumstances.
What Are the Immediate Effects of Cocaine?
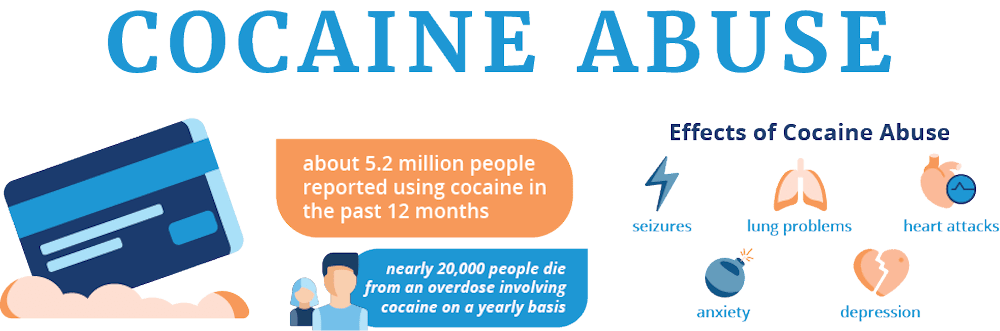
The immediate effects of cocaine use are characterized by a rapid and intense rush of euphoria and heightened energy. These effects can vary depending on the method of use (snorting, smoking, or injecting) and individual factors. Here are the common immediate effects of cocaine:
1. Euphoria:
Cocaine use leads to an intense and short-lived feeling of euphoria. This is often described as a “high” and is characterized by increased happiness and self-confidence.
2. Increased Energy:
Cocaine is a powerful stimulant that can make users feel more alert and energetic. It can lead to increased physical and mental activity.
3. Enhanced Focus:
Many users report improved concentration and focus while under the influence of cocaine.
4. Decreased Appetite:
Cocaine often suppresses appetite, leading to reduced feelings of hunger.
5. Heightened Sensory Perception:
Some individuals experience heightened sensory perception, including increased sensitivity to touch, sound, and light.
6. Talkativeness:
Cocaine use can lead to increased sociability and talkativeness. Users may become more chatty and outgoing.
7. Increased Heart Rate:
Cocaine is a vasoconstrictor, meaning it narrows blood vessels. This can lead to an increased heart rate and elevated blood pressure.
8. Dilated Pupils:
Cocaine use often causes dilated (enlarged) pupils.
9. Increased Body Temperature:
Cocaine can lead to a rise in body temperature, which may cause users to feel warm or even sweat.
10. Anxiety and Paranoia:
While some users experience feelings of confidence, others may become anxious, irritable, or paranoid. These effects can be particularly pronounced during the “comedown” when the drug’s effects wear off.
11. Short Duration:
The immediate effects of cocaine are relatively short-lived, typically lasting from a few minutes to about half an hour. This can lead to a cycle of repeated use to maintain the desired effects, which can be dangerous.
How long does cocaine stay in your system if it’s Combined With Alcohol?
The simultaneous use of cocaine and alcohol can lead to complex interactions within the body. It’s a matter of concern for many, especially when considering how this combination affects the duration that cocaine stays in your system.
- Cocaethylene Formation: One of the key factors that come into play when cocaine and alcohol are used together is the formation of a new compound called cocaethylene. This metabolite is produced in the liver when these two substances are consumed concurrently. Cocaethylene can persist in the body for a more extended period than cocaine alone, which can have implications for drug testing.
- Longer Detection Period: Cocaethylene’s presence in your system can potentially extend the detection window for cocaine in drug tests, particularly urine tests. This means that if you’ve used both cocaine and alcohol, you might test positive for cocaine for a more extended period than if you’d used cocaine alone.
- Variable Outcomes: The impact of combining cocaine and alcohol on detection times can vary from person to person. Factors such as the amount of cocaine and alcohol consumed, individual metabolism, and overall health can influence the duration of cocaethylene’s presence in your system and, consequently, its effect on drug test results.
- Health Risks: It’s crucial to emphasize that the combination of cocaine and alcohol can lead to severe health risks, including an increased risk of cardiovascular problems and overdose. The health implications of this combination often outweigh concerns about drug testing.
Your Journey to a Brighter Tomorrow
The Final Say:
It’s important to emphasize that there are no guaranteed methods to rapidly remove cocaine from your system, and attempting to do so can carry risks. Cocaine use leads to a brief, intense euphoria, increased energy, and a range of sensory and physical changes. However, it’s crucial to remember that these effects are short-lived and often followed by anxiety and a desire for more, which can lead to a cycle of use with dangerous consequences.
Prioritizing health, seeking professional help for addiction and recovery, and making informed choices should be the primary focus.
If you or someone you know is grappling with cocaine use or addiction, do not hesitate to seek guidance and support from healthcare professionals and addiction specialists. Your well-being is of utmost importance.