Do you often feel constantly low? Do you feel disconnected with your old self? Do you do activities that used to cheer you up just for the sake of doing them? Are you feeling out of touch with yourself and the people around you? Chances are that you might be suffering from Depressive Disorder or Depression. Statistics suggest that 21 million adults have suffered from major depression at some point in their lives in the United States alone. This means that 8.3% of the adult population in the United States has suffered from depression.
Depressive disorder or depression is a sneaky evil that most of us have fought. Feelings of hopelessness, lack of confidence, and loss of energy to even do daily chores are familiar to most. Depression sucks the life out of you as it affects all aspects of your life. Your relationship with your spouse, boyfriend/girlfriend, family, friends, and colleagues is affected by depression. Most importantly, depression also affects the relationship that you have with yourself.
The good news is that this condition is treatable with therapies like Interpersonal Therapy for Depression (IPT), Cognitive Behaviour Therapy(CBT), and mindfulness-based cognitive Therapy (MBCT). In this blog, we will talk about depression and how interpersonal therapy can help treat this disorder.
What is Depressive Disorder or Depression?
Depressive Disorder or Depression is a psychological condition that affects mental health. It is one of the most common mental health issues that affects 5% of adults globally. This disorder can target anyone. People who have suffered any form of abuse at some point in their lives, experienced loss or have undergone an extremely stressful situation are more vulnerable to depression.
There are various symptoms of depression. However, the most prominent ones are as follows:
It is important to note that these symptoms can also be caused by vitamin deficiencies in the body. Therefore, any form of medical condition that may trigger these symptoms must be ruled out before diagnosing an individual with depression or depressive disorder.
Once an individual has been diagnosed with depression, it is easier to treat with interpersonal therapy for depression.
Before we begin to talk about the causes behind the depressive disorder in this section, let us put forth that depression can happen to anyone. This is a disorder that does not pick and choose. An individual who might be leading a so-called ‘perfect’ life might be fighting depression.
In other words, depression is a result of a combination of various social, psychological, and environmental factors.
Let us explore the factors that can cause depression:
Depression is one of the most treatable mental health disorders. It can be managed with one treatment or a combination of more than one. Following are some of the treatments that your doctor may prescribe:
Depression alters the chemical composition of your brain. Therefore, your doctor might prescribe you anti-depressants to normalize the chemical composition in your brain. This can be done by increasing the availability of serotonin, dopamine, tyramine, etc. in your brain. These hormones are known to boost your mood and fight depression.
Psychotherapy is also known as ‘talk therapy’. It is so because, during psychotherapy, you talk to your therapist and learn coping mechanisms to improve your mental health.
Your therapist may also give you tools to utilize when you feel depressed or overwhelmed. Psychotherapy can be done alone with your therapist or in a group with your colleagues, spouse, friends, and family.
This form of treatment is often used in combination with prescribed medications or anti-depressants. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), interpersonal therapy for depression (IPT), and psychodynamic therapy are a few of the many types of treatments that your therapist may use.
Light therapy is used to treat seasonal depression. In this therapy, the individual is exposed to white light, which is known to improve depression and give a boost to the mood.
Your doctor may guide you towards alternative therapies like meditation and acupuncture along with medications to combat depression. Meditation helps manage stress and anxiety, which are some of the common causes of depression.
Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese technique where certain areas in your body are inserted with needles. This is known to stimulate those areas and treat various physical and mental conditions.
Your healthcare professional may advise you to make some lifestyle changes to deal with depression. Making these changes can avoid a relapse into depression after treatment. Regular exercise, eating a balanced and nutritious diet, and maintaining healthy boundaries in your work and personal life boost your overall well-being and reduce the chances of depression or relapsing after treatment.
Interpersonal Therapy for Depression (IPT) is a form of psychotherapy that works to identify the triggers behind depression. This form of therapy allows you to work on yourself. As a result, all the relationships in your life are enhanced. Interpersonal therapy for depression will enable you to understand yourself better.
Interpersonal therapy is a short-term psychotherapy that is used with prescribed medications. It is typically done for 12-16 sessions, depending upon the requirement of an individual. It is suggested by several studies that interpersonal therapy can work, as well as anti-depressants and medications that are prescribed for depression.
Interpersonal therapy was initially created to be a short-term treatment for depression. However, it can help people with other mental health conditions as well. Today, interpersonal therapy for depression is used for many mental health conditions:
Since interpersonal therapy for depression works on helping you understand yourself and those around you better, it is also beneficial for those who are dealing with attachment issues, grief, bereavement, conflicts with people around them, and life changes.
Since the principle behind interpersonal therapy is focused on a particular individual, the primary idea behind interpersonal therapy is to identify the interaction of the individual with others. Your therapist will help you recognize the problem areas during your interactions with others. These problem areas are then addressed one by one during the subsequent sessions.
As a result, you will learn to navigate through stressful situations and problems during interactions with others. The problem areas that are addressed are bifurcated into four categories:
Interpersonal disputes are conflicts that occur in marital relationships, social settings, and work settings. These disputes often arise due to differences of opinions and expectations. It can lead to undue stress and affect your mental health.
Sometimes, when there is a change of circumstance in your life, it may be difficult for you to adjust. For example, getting married at the end of a relationship, giving birth to a baby in the family, or simply changing cities may trigger emotions of loss and uncertainty. This can trigger episodes of depression.
Death of a loved one may lead to immense grief and contribute to depression. Grief may lead to depression when it lasts for a long time after the loss of that loved one.
When the people that you have a relationship within your life are constantly letting you down, you might experience a ‘deficit’ in that relationship.
Your therapist will identify the issues that you are facing in your personal and professional relationships from these categories and help you identify the ways to deal with such problems. They might even suggest you make certain adjustments to deal with such issues.
As mentioned previously, interpersonal therapy for depression works to equip the individual with conflict-solving skills in their personal and professional relationships. In such a scenario, an individual might be advised to make certain adjustments in their life. For example, there might be a dispute between a mother and her teenage daughter. This issue may be arising out of the daughter’s need for more freedom in terms of making her decisions. The therapist will lead the patient, i.e., the mother, to understand the root cause of the conflict. The therapist will also equip the patient with problem-solving skills and also train her to communicate effectively. This will help ensure that the symptoms of depression are not aggravated.
As the sessions progress, the patient starts developing the ability to identify the problem areas in interactions during personal and professional relationships and make adjustments accordingly.
Interpersonal therapy typically starts with your therapist taking your interview to learn more about you and the symptoms of your depression and to assess the history of relationships.
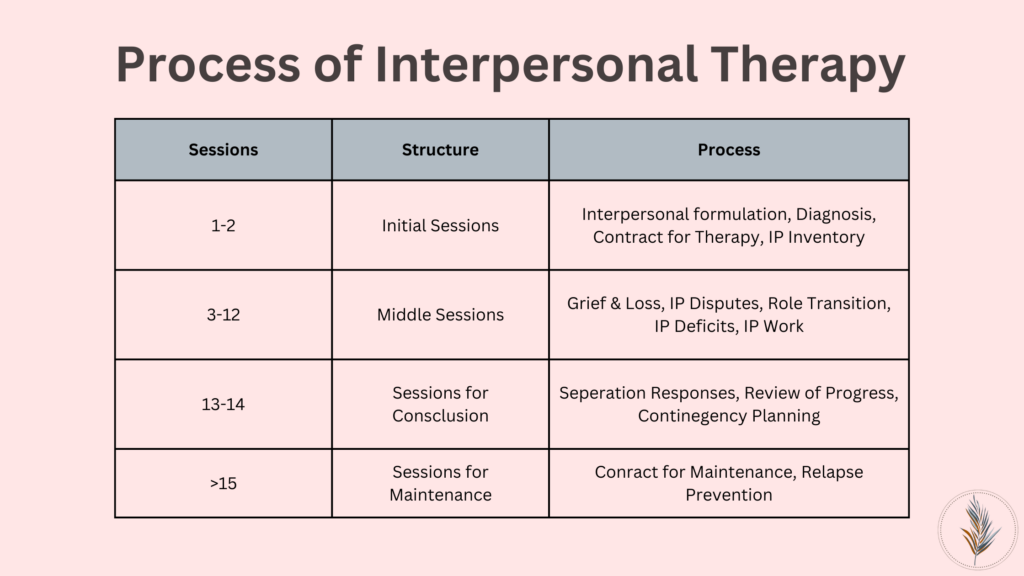
Next, your therapist will deeply assess your depression and encourage you to talk about the conflicts in your personal and professional relationships. Your therapist will work with you to identify one or two of the most important issues to address during the subsequent sessions. These are the issues that affect the symptoms of your depression the most.
The subsequent sessions will focus on addressing those issues. The therapist will help you identify the adjustments that can be made to situations where conflict arises.
As the sessions progress, the therapist will gradually shift your focus to terminating the therapy. The individual will be equipped to handle stressful situations even without the intervention of a therapist. As a result, the patient is empowered to manage the interpersonal relationships and keep them from affecting their symptoms of depression.
Interpersonal Therapy is spread over 12 to 16 sessions that are conducted every week. In extreme cases, your therapist might deem fit to increase the sessions for an additional four weeks. These sessions adhere to a specific process wherein your therapist will take regular assessments, conduct interviews, and even give you homework.
During the initial phase of interpersonal Therapy for depression, your therapist will understand more about you and the symptoms of your depression. You will be encouraged to identify the areas that affect your depression the most.
Your therapist will adapt various strategies to help you during the Therapy. Interpersonal Therapy for depression can be done via online Therapy or through in-person sessions.
IPT offers numerous benefits for individuals struggling with depression. Some of the key advantages include:
1. Focused approach: Unlike some other forms of therapy, IPT concentrates specifically on addressing the interpersonal issues contributing to your depression. By targeting these areas, IPT can provide targeted and effective treatment.
2. Short-term nature: IPT is typically a short-term therapy, lasting anywhere from 12 to 16 weeks. This means that you can see significant improvements in your mental well-being in a relatively short period.
3. Improved communication skills: IPT places a strong emphasis on improving communication skills, which can positively impact all areas of your life. By learning effective communication techniques, you can express your needs and emotions more clearly, leading to healthier relationships and increased overall happiness.
IPT addresses four main problem areas that commonly contribute to depression:
1. Grief: Losing a loved one can be an incredibly difficult experience that can trigger or worsen depression. IPT helps individuals process their grief and navigate the complex emotions associated with loss.
2. Role disputes: Conflicts and disagreements within relationships can significantly impact our mental health. IPT aims to identify and address any role disputes that may be contributing to your depression, allowing for healthier and more fulfilling relationships.
3. Role transitions: Major life changes, such as marriage, divorce, or becoming a parent, can be challenging and disruptive to our mental well-being. IPT helps individuals navigate these transitions and adapt to their new roles effectively.
4. Interpersonal deficits: Some individuals may struggle with forming and maintaining healthy relationships. IPT focuses on developing the necessary skills to establish and nurture meaningful connections with others, reducing feelings of isolation and loneliness.
IPT typically involves weekly sessions with a trained therapist. These sessions follow a structured format, which includes:
1. Assessment: In the initial sessions, your therapist will gather information about your background, current symptoms, and interpersonal relationships. This assessment phase helps the therapist understand your unique situation and tailor the therapy to your specific needs.
2. Setting treatment goals: Together with your therapist, you will identify specific treatment goals based on the problem areas that need to be addressed. These goals will guide the course of your therapy and help you measure your progress.
3. Exploration and analysis: Throughout the therapy, you will work with your therapist to explore your relationships and identify any patterns or dynamics that may be contributing to your depression. This process involves examining your thoughts, feelings, and behaviors in the context of your interactions with others.
4. Skill-building: IPT incorporates various techniques and strategies to improve your communication skills, problem-solving abilities, and relationship-building capabilities. Your therapist will guide you in developing these skills and provide support as you practice them in your daily life.
If you are interested in trying IPT, it’s important to find a qualified therapist who specializes in this approach. Here are a few steps you can take to find an IPT provider:
1. Ask for recommendations: Reach out to your primary care physician, mental health professionals, or trusted friends and family members for recommendations. They may be able to suggest reliable therapists who offer IPT.
2. Search online: Use reputable online directories or search engines to find therapists in your area who specialize in interpersonal therapy. Read reviews and check their credentials to ensure they meet your requirements.
3. Contact professional organizations: Get in touch with professional organizations, such as the American Psychological Association or the International Society of Interpersonal Psychotherapy, for referrals to qualified IPT providers.
Interpersonal therapy for depression is particularly useful in a group setting. This is so because in a group setting when the treatment is being conducted with each other, it will enable the patients to understand each other better.
Interpersonal therapy for depression in a group setting will also enable the group to make certain adjustments that will encourage conflict resolution within the group. In case conflicts arise within the group, the therapist may encourage and give training in communication within the group. This will help the group members resolve the dispute by themselves.
Interpersonal therapy might not prove to be beneficial for everyone. This is because each person experiences challenges with their mental health differently, and therefore, the treatment will also be different for each individual.
Motivation is a crucial part of interpersonal therapy, and this form of psychotherapy encourages an individual to look into the role they play in their personal and professional relationships. If you are unable to dive into the depths of the role you play in every relationship of your life, then interpersonal therapy for depression is not for you.
More often than not, depression is a recurring condition. Therefore, the patients are advised to undergo maintenance sessions after interpersonal therapy ends. Maintenance sessions are monthly sessions in which your therapist will ensure that you are implementing the adjustments made during the previous sessions. This ensures that the stress from social interactions does not take a toll on your mental health. This will also ensure that you don’t relapse into depression after the therapy ends.
While IPT can be effective as a standalone therapy, it can also be integrated with other treatment approaches to provide comprehensive care for individuals with depression. Some common treatment combinations include:
1. Medication: In some cases, medication may be prescribed alongside IPT to manage the symptoms of depression. This combination can be particularly beneficial for individuals with severe or treatment-resistant depression.
2. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT): IPT and CBT complement each other well. CBT focuses on identifying and changing negative thought patterns, while IPT addresses the impact of interpersonal relationships. Combining these two therapies can provide a more holistic approach to treating depression.
Frequently Asked Questions
CBT helps you identify the thoughts that might hurt the symptoms of depression. IPT, on the other hand, focuses on identifying solutions to your interpersonal challenges.
People suffering from major depression, anxiety disorder, or eating disorders can benefit from interpersonal therapy.
One major disadvantage of interpersonal therapy is that it might not be beneficial for everyone. People with severe mental illnesses and people who have experienced trauma might not benefit from interpersonal therapy.
Interpersonal therapy is a short-term treatment. A treatment lasts for 12-16 sessions that last for one hour. The beginning phase lasts for 1 to 3 sessions wherein your therapist understands the symptoms of your depression. Phase 2 concentrates on finding solutions to your interpersonal difficulties and phase 3 focuses on making you independent enough to ensure that you can deal with interpersonal challenges without the intervention of your therapist.
Depression or depressive disorder is one of the tough battles that you might fight. Depression has the potential to take away your zeal to live. Simple tasks become impossible to manage, and this affects your quality of life.
To combat the same, interpersonal therapy for depression will not only help you manage your stress levels but will also ensure that you have better personal and professional relationships. After the sessions end, your therapist will also ensure that you do not relapse by conducting maintenance sessions with you.
Calusa Recovery is a center for depression treatment in South Florida and an addiction treatment center for effective care of co-occurring disorders. At the Calusa Recovery depression center in South Florida, we specialize in treating mental health disorders that co-occur with addiction, improving outcomes. Our facility is newly renovated and is safe and supportive for each client during this life-changing time.