Panic disorders are a serious condition affecting mental health and can be understood as a type of anxiety disorder in the 5th edition of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, also known as DSM criteria for panic disorder.
The DSM criteria for panic disorder is a type of authoritative guideline that is used by mental health professionals in the United States to diagnose panic disorders.
As per DSM criteria for panic disorder, an individual must experience recurring and unexpected panic attacks to be diagnosed with panic disorder. Studies conducted by the American Psychological Association (APA) state that 1 out of 75 people have experienced panic disorder in their lifetime.
Panic disorder is a common condition that requires careful diagnosis which makes the DSM criteria for panic disorder important. In this blog, we have explained more on this topic and answered some frequently asked questions.
What are panic disorders and DSM criteria for panic disorder?
People suffering from panic disorder experience panic attacks. Panic attacks are episodes in which an individual faces immense fear and discomfort. The worst thing about panic attacks is that they can either stem from stress, anxiety, or worry or can occur even in a calm state of mind.
For example, if a person is suffering from panic disorder, then the panic attacks can be unexpected and entirely unprovoked. These panic attacks can occur in the middle of the night or while standing in a queue to buy groceries. Due to this reason, some people isolate themselves due to the social stigma of mental health disorders.
The DSM criteria for panic disorder is a system used to decide whether an individual can be diagnosed with panic disorder or not. Today, these criteria are used by certified mental health professionals worldwide to diagnose and classify almost every illness related to mental health.
What are the DSM criteria for panic disorder diagnosis?
The criteria for diagnosis of a panic disorder are specified in the DSM category for panic disorder. As per this criteria, to be diagnosed with a panic disorder, the panic attacks must be recurring and unexpected. The following is the detailed DSM criteria for panic disorder.
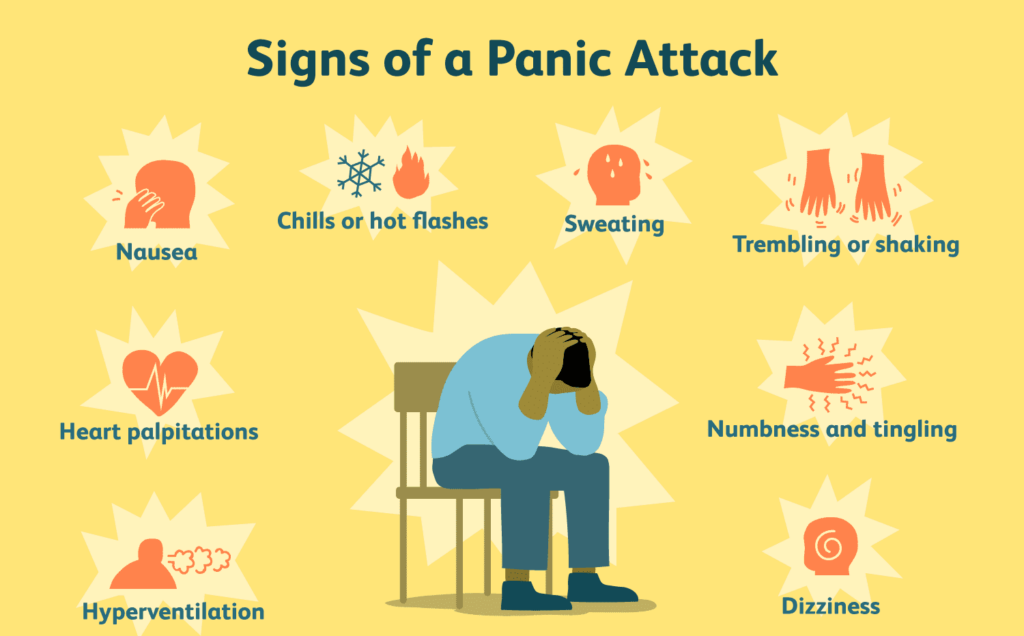
1. First and foremost, the episodes of panic attacks must be recurring and unexpected. During episodes of panic attacks, the patient might feel immense fear and discomfort. During this episode, an individual must feel any 4 of the following symptoms:
- Palpitations and an increased heart rate
- Sweating
- Trembling and shaking
- Shortness of breath
- A feeling of being choked
- A pain in the chest and discomfort
- Nausea and abdominal issues
- Hot and cold flashes
- A numbness in some parts or all over the body along with tingling sensations
- Chills or hot flashes
- A feeling of losing reality or being detached from one’s own identity
- An irrational fear of losing control of oneself and one’s surroundings
- An irrational fear of dying
During episodes of panic attacks, other symptoms like crying, screaming, sobbing, headache, etc. may also be experienced. However, these symptoms are not a part of the 13 symptoms mentioned above.
2. Episodes of at least 1 panic attack which is followed by a period of 1 month of the following:
- Continuous worry or stress over another panic attack and its aftermath
- Making extreme changes in the behavior that is related to panic attacks. This means that the patient is taking measures to avoid having panic attacks as much as possible
3. These panic attacks should not be a result of substance and drug abuse or any other medical condition like hyperthyroidism
4. The episodes of panic attacks should not be a result of any other medical condition like phobias, obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), separation anxiety, or post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Why is the DSM Criteria for panic disorder important?
As per research, panic disorder is the most common type of illness that affects mental health. About 19.1% of the total adult population of the United States suffer from some type of anxiety or panic disorder. Out of these, very few individuals seek treatment for their condition.
Since panic and anxiety disorders are common conditions, DSM criteria for panic disorder are even more important as they help determine whether an individual can be diagnosed with a panic disorder or not. It helps to professionally assess the symptoms and prescribe the course of treatment.
The patient must be honest with their medical professional when describing their symptoms to aid a correct diagnosis. Understandably, it might be difficult to describe the feelings of anxiety initially. However, once the patient is comfortable enough to discuss their symptoms, it opens doors to managing panic disorder and avoiding panic attacks in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What are the causes of panic disorder?
Factors like genetic factors, stress, environment, history of poor mental health, trauma, or loss or bereavement of a loved one can contribute to panic disorders.
2. What are the symptoms of panic attacks?
Symptoms like increased heart rate, sweating, hot flashes and chills, ragged breath, dizziness, and chest pain are symptoms of panic attacks.
3. What are the DSM criteria for panic disorder?
The DSM criteria for panic disorder include excessive and unnatural anxiety and worry over episodes of subsequent panic attacks after the first episode of a panic attack. Additionally, episodes of panic disorder comprise at least 4 of the 13 symptoms as mentioned in DSM criteria for panic disorder like palpitations, sweating, trembling, breathlessness, pain in the chest, nausea, etc.
4. What is the 333 rule for panic attacks?
The 333 rule for anxiety is helpful when you feel the onset of a panic attack. This is a trick that therapists recommend to control their anxiety attacks. In the 333 rule, the patients are taught to pay attention to and identify 3 objects and sounds, and move 3 body parts. This helps in diverting their focus and controlling their anxiety.
Conclusion
If an individual has been diagnosed with panic disorder, it does not mean that they can never live a normal life. With proper strategy and medical intervention, this condition is manageable. Panic disorder does not have to be a hindrance to living a fulfilling life.
Additionally, the Government also provides aid to individuals who qualify for aid and are diagnosed with panic disorders as per the DSM criteria for panic disorder.
At Calusa Recovery, we understand the profound impact that panic attacks can have on your well-being. Our comprehensive approach to mental health encompasses tailored treatment options designed to help you regain control over your life. Through evidence-based therapies, personalized strategies, and compassionate support, we guide you on a transformative journey toward managing and overcoming panic attacks.